ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) .Computers can only understand numbers, so an ASCII code is the numerical representation of a character such as 'a' or '@' or an action of some sort. ASCII was developed a long time ago and now the non-printing characters are rarely used for their original purpose.
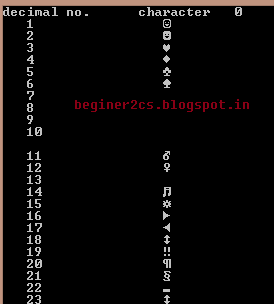
THis picture contain ASCII values only correspond to 0 to 127 :
BUT in our program we show all possible ASCII values & corresponding character.
C code :
THis picture contain ASCII values only correspond to 0 to 127 :
BUT in our program we show all possible ASCII values & corresponding character.
C code :
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int main()
{
int i=0;
char ch;
printf("decimal no.\t character");
for(i=0;i<256;i++)
{
printf(" %d\t\t %c\n",i,ch);
ch = ch + 1;
}
return 0;
}
OUTPUT :-
Print ASCII Value In Python 2.7 :
- #Print ASCII VALUE
- print 'ASCII value -> Char'
- for i in range(256):
- print ' '+str(i)+' -> "'+chr(i)+'"'
Thanks :)

No comments:
Post a Comment
THANKS FOR UR GREAT COMMENT